How do doctors diagnose the problem?
There are several different types of test that you doctor may order to provide infomration on the extent of your whiplash injury.
Radiological Imaging
Radiological imaging tests help your doctor see the anatomy of your spine. There are many kinds of imaging tests including:
- X-rays
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Digital motion x-ray (DMX)
- Myelogram
- Bone Scan
- Electromyogram
X-rays
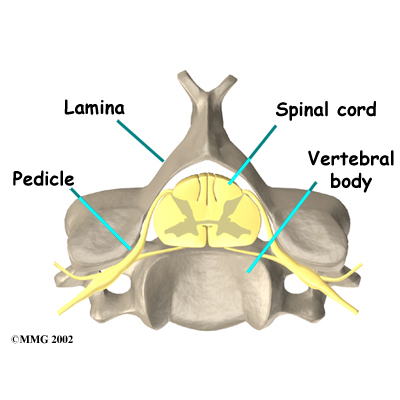
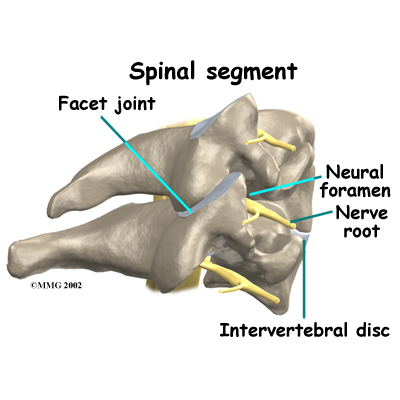
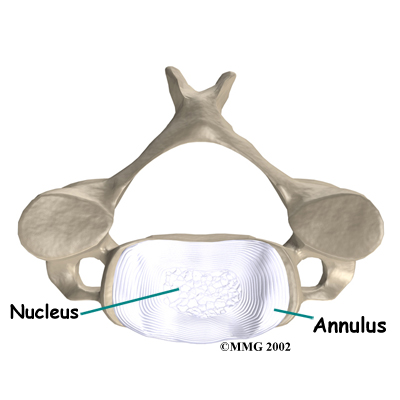
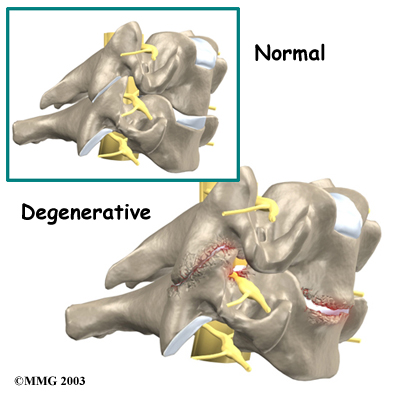
X-rays show problems with bones, such as infection, bone tumors, or fractures. X-rays of the spine also can give your doctor information about how much degeneration has occurred in the spine, such as the amount of space in the neural foramina and between the discs.
X-rays are usually the first test ordered before any of the more specialized tests. Special x-rays called flexion/extension x-rays may help to determine if there is instability between vertebrae. These x-rays are taken from the side as you bend as far forward and then as far backward as you can. Comparing the two x-rays allows the doctor to see how much motion occurs between each spinal segment.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
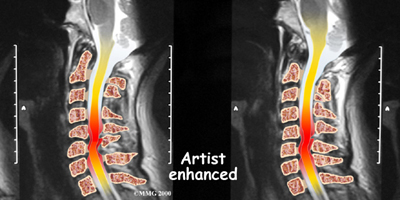
If more information is needed, your doctor may order an MRI. The MRI machine uses magnetic waves rather than x-rays to create pictures of the cervical spine in slices. MRIs show the cervical spine vertebrae, as well as the soft tissue structures, such as the discs, joints, and nerves. MRI scans are painless and don't require needles or dye. MRI scan has become the most common test to look at the cervical spine after x-rays have been taken.
Computed Tomography (CT)
CT scan is a special type of x-ray that lets doctors see slices of bone tissue. The machine uses a computer and x-rays to create these slices. It is used primarily when problems are suspected in the bones.
Digital motion x-ray (DMX)
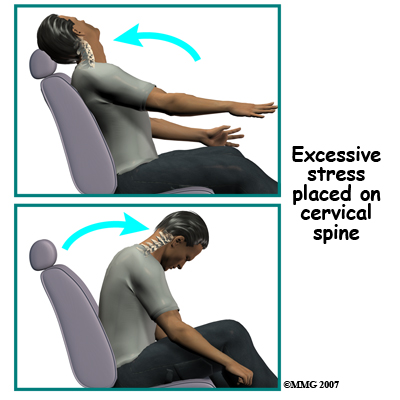
DMX is a new fluoroscopic based x-ray system designed to objectively detect and document soft tissue/ligament injury most commonly associated with whiplash injuries of the spine. DMX evaluates biomechanical relationships and abnormal movements of the cervical spine. Specifically, DMX:
- Shows abnormal movement of vertebral bodies, facets, and other spinal elements
- Shows joint hypermobility, hypomobility, or restriction
- Shows normal or abnormal initiation of cervical motion
Example of DMX diagnostic video fluoroscopy.
DMX uses digital and optic technology now available. DMX is the latest generation of videofluoroscopy (VF) that uses low doses of radiation. The images have improved clarity and resolution over VF and are recorded digitally on CD or DVD disc. DMX digital images can be replayed and studied on standard computer systems. DMX images are simply x-ray images taken at 30 frames per second to form a multiple radiographic array or series that can be run as a movie file to display real time motion of the joints of the body.
DMX radiographic series can be paused at any location and the measurements and interpretation common to radiology can be applied to the still images. These images would be identical to plain film images if plain film radiography were performed at the same location at the same moment in motion. DMX acquires approximately 2700 images for the same amount of radiation as seven regular x-rays.
For more information visit http://www.dmxofmontana.com
Myelogram
The myelogram is a special kind of x-ray test where a special dye is injected into the spinal sac. The dye shows up on an x-ray. It helps a doctor see if there is a herniated disc, pressure on the spinal cord or spinal nerves, or a spinal tumor. Before the CT scan and the MRI scan were developed, the myelogram was the only test that surgeons had to look for a herniated disc. The myelogram is still used today but not nearly as often. The myelogram is usually combined with CT scan to give more detail.
Bone Scan
A bone scan is a special test where radioactive tracers are injected into your blood stream. The tracers then show up on special x-rays of your neck. The tracers build up in areas where bone is undergoing a rapid repair process, such as a healing fracture or the area surrounding an infection or tumor. Usually the bone scan is used to locate the problem and other tests such as the CT scan or MRI scan are then used to look at the area in detail.
Electromyogram (EMG)
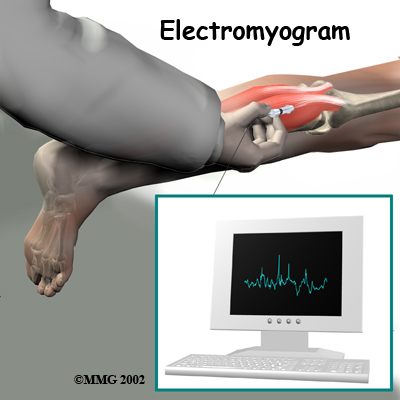
An electromyogram (EMG) is a special test used to determine if there are problems with any of the nerves going to the upper limbs. EMGs are usually done to see if one or more nerve roots have been pinched by a herniated disc. During the test, small needles are placed into certain muscles that are supplied by each nerve root. If there has been a change in the function of the nerve, the muscle will send off different types of electrical signals. The EMG test reads these signals and can help determine which nerve root is involved.
Grading the Severity of Injury
The physical exam combined with the imaging studies help determine the severity or grade of the injury. There is more than one way to assign a grade to a patient’s whiplash. Here are two examples of the more commonly used models used to classify or grade whiplash injuries:
Croft Guidelines
- Grade I: Minimal – No limitation of motion, no ligamentous injury, no neurological findings
- Grade II: Slight – Slight limitation of motion, no ligamentous injury, no neurologic findings
- Grade III: Moderate – Limitation of motion, ligamentous instability, neurologic symptoms present
- Grade IV: Moderate-to-Severe – Limitation of motion, some ligamentous injury, neurological symptoms, fracture or disc derangement
Quebec Whiplash Classification
- Grade 0: No complaint or physical sign
- Grade I: Neck complaint of pain, stiffness or tenderness, no physical signs
- Grade II: Neck pain and musculoskeletal signs
- Grade III: Neck pain and neurological signs
- Grade IV: Neck pain and fracture or dislocation
Medication
Your doctor may prescribe certain types of medication if the nerves are irritated or compressed and you have neck pain that travels down your arm (radiculopathy). Severe symptoms may be treated with narcotic drugs, such as codeine or morphine. But these drugs should only be used for the first few days or weeks after problems with radiculopathy start because they are addictive when used too much or improperly. Muscle relaxants may be prescribed to calm neck muscles that are in spasm. You may be prescribed anti-inflammatory medications such as aspirin or ibuprofen. Ensure that you consult with your doctor or pharmacist regarding the use of pain relief or anti-inflammatory medication.
Injection
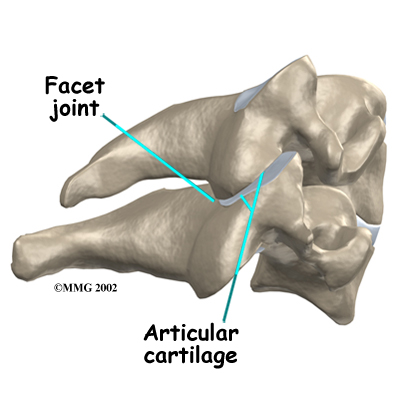
Pain resulting from irritation of the facet joints may be alleviated with injection of an anesthetic agent similar to Novacaine such as Bipuvacaine. Your doctor may use this numbing agent to both confirm the source of pain as coming from the joint and help reduce or eliminate your pain.








 (403) 679-7179
(403) 679-7179  concierge@one-wellness.ca
concierge@one-wellness.ca 

