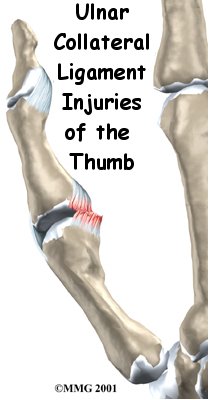
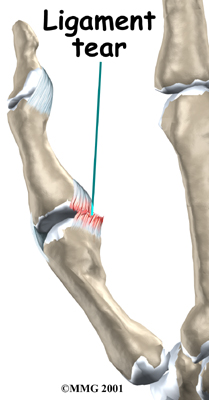
If the ligaments are completely torn, you will most likely have surgery to repair them. A torn ligament cannot fully heal itself. Surgery for the thumb collateral ligaments is usually done as an outpatient procedure, meaning you will probably go home the same day as the surgery.
Suture Repair
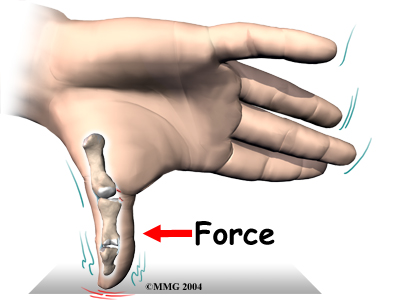
In the surgery, your surgeon will make a small V- or over the back of the MCP joint of the thumb.
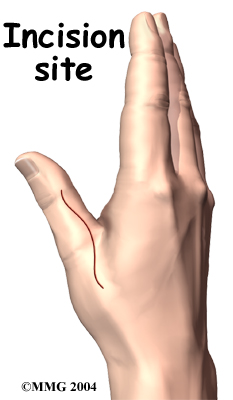
This helps isolate and protect the nerve branches running up your thumb. Your surgeon will then cut through a sheet of tissue called the .
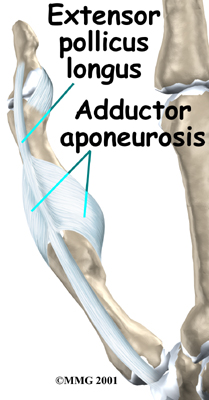
This helps expose the MCP joint and the ligaments. The area around the injury is examined for any soft tissue damage. Your surgeon then with stitches that anchor them back to the bone.
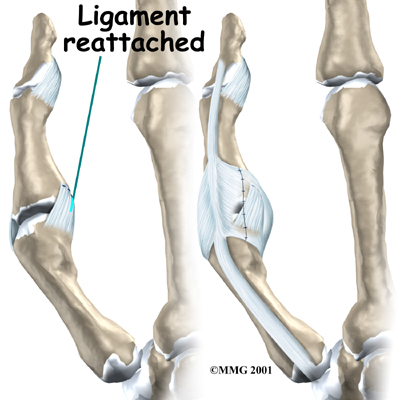
Patients usually have good results when suture repair is done within four weeks after the injury. After surgery, pain and stiffness are usually minimal, and thumb strength will normally return.
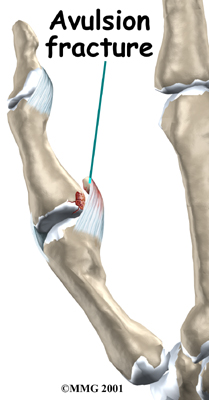
In some patients, the MCP joint continues to be unstable. The joint feels painful when pinching or grasping and is generally weak. Most of the time, chronic instability tends to happen when the patient doesn't get treatment or when a doctor wasn't aware of a ruptured tendon. However, even when skilled surgery is performed, the thumb sometimes ends up being chronically unstable.
Fusion Surgery
A thumb that is loose and unstable will eventually develop arthritis. Some surgeons have had success by grafting in new tissue to reconstruct the ligaments. When the ligament has been unstable for a long time, surgery may be needed to keep the MCP joint from moving. This type of surgery is called fusion. A fusion procedure is often the best choice when a patient's job involves heavy labor that would continue to put too much strain on his or her unstable thumb joint.
When the joint is fused together, a person's ability to do day-to-day tasks isn't affected that much. This is because some people have a very small range of motion in the MCP joint anyway. Fusion keeps the joint from moving, but it also protects it from eventually becoming arthritic and painful.
Surgery does carry some risks. In rare cases, some of the small nerves to the skin on the back of the thumb may be damaged during surgery. This may cause numbness on the back of the thumb. When this happens, it usually gets better on its own. Sometimes the MCP and other thumb joints become stiff. Physical or occupational therapy treatments are helpful for easing the stiffness and helping you regain thumb movement.
Portions of this document copyright MMG, LLC.





 (403) 679-7179
(403) 679-7179  concierge@one-wellness.ca
concierge@one-wellness.ca